Floyd's Cycle detection algorithm with GoLang
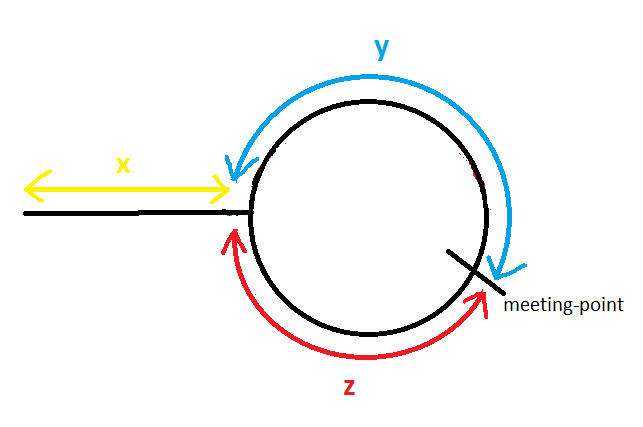
서로 다른 속도로 이동하는 포인터를 다음과 같이 가정,
느린 포인터 이동 속도 = 1
빠른 포인터 이동 속도 = 2
각 포인터의 시작 지점을 다음과 같이 지정,
느린 포인터 시작 지점 = 0
빠른 포인터 시작 지점 = 1
그랬을 때, 두 포인터가 위의 그림과 같은 순환 경로를 진행 시 meeting-point 에서 만났을 때 다음과 같음을 알 수 있음,
느린 포인터가 만나기 까지 이동한 거리 = x + y
빠른 포인터가 만나기 까지 이동한 거리 = x + y + z + y = x + 2y + z
빠른 포인터는 느린 포인터보다 두 배 빠른 속도로 이동 했기 때문에,
느린 포인터가 이동한 거리의 두 배가 곧 빠른 포인터가 이동한 거리가 됨. 이를 수식으로 표현하면 다음과 같음.
2 * (느린 포인터 이동 거리) = 빠른 포인터 이동 거리
2 * (x + y) = x + 2y + z
위 수식을 정리하면 다음과 같음
x = z
시작 지점 부터 순환 시작 지점 까지의 거리 = 첫 만난 지점 부터 순환 시작 지점 까지의 거리
그렇기에, 처음 만난 지점에서 한 포인터를 시작 지점으로 옮기고 두 포인터를 동일한 속도로 이동 시키면 항상 순환 시작 지점에서 만남.
이를 통해, Floyd's Cycle Detection 알고리즘의 시간 복잡도는 O(리스트 길이) 즉, O(N) 임을 알 수 있음
왜냐하면, 순환 시작 지점 탐색에 대한 시간 복잡도는 <= N + M <= 2N 을 만족 하고 (N: 총 노드 수, M: 순환 노드 수)
순환 탐지에 대한 시간 복잡도는 <= N - M <= 2N 을 만족 하기 때문
뿐만 아니라, 순환 지점에서 만난 후 한 포인터를 다시 순환 시킨 후 돌아와서 다시 만나기 까지의 거리를 통해 순환 길이를 알 수 있음
파이썬 코드는 다음과 같음:
def floyd(f, x0):
# Main phase of algorithm: finding a repetition x_i = x_2i.
# The hare moves twice as quickly as the tortoise and
# the distance between them increases by 1 at each step.
# Eventually they will both be inside the cycle and then,
# at some point, the distance between them will be
# divisible by the period λ.
tortoise = f(x0) # f(x0) is the element/node next to x0.
hare = f(f(x0))
while tortoise != hare:
tortoise = f(tortoise)
hare = f(f(hare))
# At this point the tortoise position, ν, which is also equal
# to the distance between hare and tortoise, is divisible by
# the period λ. So hare moving in circle one step at a time,
# and tortoise (reset to x0) moving towards the circle, will
# intersect at the beginning of the circle. Because the
# distance between them is constant at 2ν, a multiple of λ,
# they will agree as soon as the tortoise reaches index μ.
# Find the position μ of first repetition.
mu = 0
tortoise = x0
while tortoise != hare:
tortoise = f(tortoise)
hare = f(hare) # Hare and tortoise move at same speed
mu += 1
# Find the length of the shortest cycle starting from x_μ
# The hare moves one step at a time while tortoise is still.
# lam is incremented until λ is found.
lam = 1
hare = f(tortoise)
while tortoise != hare:
hare = f(hare)
lam += 1
return lam, mu
golang 코드는 다음과 같음:
floyds.go:
package cycledetection
import "log"
type Node struct {
Value int
Point *Node
}
func (n *Node) TortoiseMove() *Node {
return n.Point
}
func (n *Node) HareMove() *Node {
if n.Point == nil {
return nil
}
return n.Point.Point
}
func alg(cycle *Node) (bool, int, int) {
tortoise := cycle
hare := cycle.Point
tortoiseDistance := 0
hareDistance := 0
for tortoise.Value != hare.Value {
tortoise = tortoise.TortoiseMove()
log.Printf("move tortoise: %d\n", tortoise.Value)
hare = hare.HareMove()
if hare == nil {
return false, 0, 0
}
log.Printf("move hare: %d\n", hare.Value)
tortoiseDistance += 1
hareDistance += 2
}
log.Println("---------First Time Meet----------")
meetDistance := 0
for meetDistance == 0 || tortoise.Value != hare.Value {
if meetDistance == 0 {
tortoise = cycle
} else {
tortoise = tortoise.TortoiseMove()
}
log.Printf("move tortoise: %d\n", tortoise.Value)
hare = hare.TortoiseMove()
log.Printf("move hare: %d\n", hare.Value)
meetDistance += 1
}
log.Println("---------Second Time Meet----------")
cycleLength := 0
for cycleLength == 0 || hare.Value != tortoise.Value {
hare = hare.TortoiseMove()
log.Printf("move hare: %d\n", hare.Value)
cycleLength += 1
}
log.Println("---------Hare Loop End----------")
return true, meetDistance - 1, cycleLength
}
floyds_test.go:
package cycledetection
import (
"log"
"testing"
)
func Test_Floyds(t *testing.T) {
log.Printf("Cycle Detection Test-1 Started!!!!\n")
isCycle, startPoint, cycleLength := alg(FloydsCycle)
if isCycle {
log.Printf("Cycle Detected!!!!\n")
log.Printf("RESULT: cycleStartPoint: %d, cycleLength: %d\n", startPoint, cycleLength)
} else {
log.Printf("Cycle is not Detected!!!!\n")
}
log.Printf("Cycle Detection Test-1 Ended!!!!\n")
log.Printf("Cycle Detection Test-2 Started!!!!\n")
isCycle, startPoint, cycleLength = alg(NonCycle)
if isCycle {
log.Printf("Cycle Detected!!!!\n")
log.Printf("RESULT: cycleStartPoint: %d, cycleLength: %d\n", startPoint, cycleLength)
} else {
log.Printf("Cycle is not Detected!!!!\n")
}
log.Printf("Cycle Detection Test-2 Ended!!!!\n")
}
var (
LENGTH = 10
CYCLE_START_POINT = 3
FloydsCycle *Node
NonCycle *Node
)
func init() {
cycle := make([]*Node, 0)
for i := 0; i < LENGTH; i++ {
cycle = append(cycle, &Node{Value: i})
}
for i := 0; i < LENGTH; i++ {
if i != len(cycle)-1 {
cycle[i].Point = cycle[i+1]
} else {
cycle[i].Point = cycle[CYCLE_START_POINT]
}
}
FloydsCycle = cycle[0]
noncycle := make([]*Node, 0)
for i := 0; i < LENGTH; i++ {
noncycle = append(noncycle, &Node{Value: i})
}
for i := 0; i < LENGTH; i++ {
if i != len(noncycle)-1 {
noncycle[i].Point = noncycle[i+1]
}
}
NonCycle = noncycle[0]
}
<reference>
2. en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cycle_detection#Brent's_algorithm